PVC
Today, only 70 years after its public appearance on the market, PVC is the most widely used plastic materials in the world.
Almost a century divides the synthesis of vinyl chloride, achieved in laboratory by V.H. Regnault, a French scientist, in 1835, from the production of the first items made of PVC.
The polymerization of vinyl chloride was already achieved in laboratory since the years immediately before WW1, but actual production of PVC started in the US during 1927, and mass-production began only from 1939.
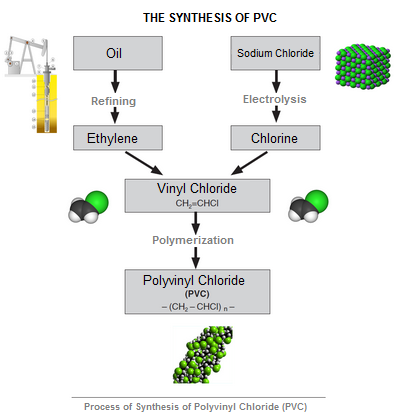
The vinyl chloride monomer, briefly VCM, easily polymerizes forming PVC. Polymerization means the chemical process through which a substance formed by two or more molecules, which are called monomers, of the same compound is obtained.
The polymer term means substance composed by many fundamental units which are repeated many times in the structure, like a wall formed by many identical bricks.
To make it occur, the following procedure must be followed: VCM, water and specific additives, such as "catalysts" or reaction accelerators, emulsifiers, dispersers etc., are introduced in the autoclave and under the combined action of heath and mechanical shaking, polymerization is performed. Most part of the VCM molecules aggregate forming the chain macromolecules of the PVC which, dried and purified, appears as a white dust. The raw materials PVC comes from are oil and sodium chloride, better known with the name of rock salt or, simply, salt.
From salt, chlorine and sodium are obtained by electrolysis, in fixed proportions. The chlorine obtained through electrolysis replaces part of the hydrogen contained in ethylene, an unsaturated hydrocarbon present in cracking gases of petroleum products, generating in this way the vinyl chloride monomer, whose empirical formula is (CH2 = CHCl), and hydrochloric acid (H-Cl). Items made of polyvinylchloride are smooth, bright, impermeable to oil, grease and smells, may be transparent or opaque, are self-extinguishing and they don't propagate flames, are usually rigid and stand well against abrasion, are inert and recyclable, so they don’t harm nature.
In the case of profiles for doors and windows, PVC compound containing special additives that impart the proper balance of weather resistance, rigidity and mechanical strenght required during the useful life of the produtct.

Informações
The features and physical and mechanical properties of TOSATTI PVC profiles. PDF Document
The PVC in the architecture of BRAZIL - PVC Institute. PDF Document